Mesothelioma is a forceful tumor influencing the layer coating of the lungs and midriff.
Threatening mesothelioma is the most genuine of all asbestos-related infections. Introduction to asbestos is the essential driver and danger component for mesothelioma.
Making a right mesothelioma determination is especially troublesome for specialists in light of the fact that the malady frequently gives indications that copy other normal infirmities. There is right now no known cure for mesothelioma, however medicines, for example, surgery and chemotherapy can help to enhance the common mesothelioma anticipation and even build one's future.
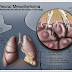
Three noteworthy sorts of mesothelioma exist and they are separated by the organs basically influenced. Pleural mesothelioma (influencing the lung's defensive coating in the midsection pit) speaks to around seventy five percent of all mesothelioma frequency. Peritoneal mesothelioma, which influences the stomach hole, and pericardial mesothelioma, which influences the heart depression, embody the rest of.
Mesothelioma Cancer
Get This Image For Your Site
There are three perceived mesothelioma cell sorts. Somewhere around 50% and 70% of all mesotheliomas are of the epithelial mixture. While anticipation is by and large poor, it is viewed as less forceful than sarcomatoid mesothelioma and biphasic mesothelioma, which embody the rest of cell-sort analyze.
The cavities inside of the body enveloping the midsection, mid-region, and heart are encompassed by a film of cells known as the mesothelium. Mesothelial cells help with general organ capacities. The mesothelium is especially critical to organs that are normally in movement, for example, development or withdrawal of the lungs, stomach, or heart. Oil from the mesothelial cells permits unfenced of movement inside of the body. The mesothelium of the midsection, stomach area, and cardiovascular depression are known as the pleura, the peritoneum, and the pericardium, individually. Each of these groupings of mesothelial cells is amazingly basic to the elements of the body structures which they incorporate.
Malignancies (harmful tumors) happening inside of the mesothelial layers are known as dangerous mesothelioma, or just mesothelioma. Benevolent tumors of the mesothelium are known not, yet are considerably more uncommon than harmful mesothelial tumors.
While tumors of the mesothelium were initially perceived in the late 18th century, it was not until the center of the 20th century that this specific growth was contemplated and analyzed with more detail. It was as of now when suspicions of the growth's causal association with asbestos introduction turned out to be more substantiated. A joint exploration wander through the Department of Thoracic Surgery at the University of the Witswater and Johannesburg General Hospital in South Africa gave the most convincing proof of the nexus between asbestos presentation and the advancement of pleural mesothelioma.
Frequency of mesothelioma is still truly uncommon, with just 2,500-3,000 conclusions in the United States every year. There was a spike in reported determinations somewhere around 1970 and 1984, which has been credited to the inertness period in the middle of analysis and the stature of modern exposures, which happened about 40-60 years preceding this time. While presentation was normal over the United States in about all commercial enterprises, it was especially common in the WWII-period military modern cycle, including naval force shipyards.
In spite of the fact that this growth is significantly more regular in men beyond 60 years old, mesothelioma in ladies and kids has been reported too. Mesothelioma foundations for determination in ladies and youngsters are mostly ascribed to optional introduction to asbestos, as it was not unprecedented for men to bring asbestos over into the home on their bodies or dress.
Continue reading ...
Threatening mesothelioma is the most genuine of all asbestos-related infections. Introduction to asbestos is the essential driver and danger component for mesothelioma.
Making a right mesothelioma determination is especially troublesome for specialists in light of the fact that the malady frequently gives indications that copy other normal infirmities. There is right now no known cure for mesothelioma, however medicines, for example, surgery and chemotherapy can help to enhance the common mesothelioma anticipation and even build one's future.
Three noteworthy sorts of mesothelioma exist and they are separated by the organs basically influenced. Pleural mesothelioma (influencing the lung's defensive coating in the midsection pit) speaks to around seventy five percent of all mesothelioma frequency. Peritoneal mesothelioma, which influences the stomach hole, and pericardial mesothelioma, which influences the heart depression, embody the rest of.
Mesothelioma Cancer
Get This Image For Your Site
There are three perceived mesothelioma cell sorts. Somewhere around 50% and 70% of all mesotheliomas are of the epithelial mixture. While anticipation is by and large poor, it is viewed as less forceful than sarcomatoid mesothelioma and biphasic mesothelioma, which embody the rest of cell-sort analyze.
The cavities inside of the body enveloping the midsection, mid-region, and heart are encompassed by a film of cells known as the mesothelium. Mesothelial cells help with general organ capacities. The mesothelium is especially critical to organs that are normally in movement, for example, development or withdrawal of the lungs, stomach, or heart. Oil from the mesothelial cells permits unfenced of movement inside of the body. The mesothelium of the midsection, stomach area, and cardiovascular depression are known as the pleura, the peritoneum, and the pericardium, individually. Each of these groupings of mesothelial cells is amazingly basic to the elements of the body structures which they incorporate.
Malignancies (harmful tumors) happening inside of the mesothelial layers are known as dangerous mesothelioma, or just mesothelioma. Benevolent tumors of the mesothelium are known not, yet are considerably more uncommon than harmful mesothelial tumors.
While tumors of the mesothelium were initially perceived in the late 18th century, it was not until the center of the 20th century that this specific growth was contemplated and analyzed with more detail. It was as of now when suspicions of the growth's causal association with asbestos introduction turned out to be more substantiated. A joint exploration wander through the Department of Thoracic Surgery at the University of the Witswater and Johannesburg General Hospital in South Africa gave the most convincing proof of the nexus between asbestos presentation and the advancement of pleural mesothelioma.
Frequency of mesothelioma is still truly uncommon, with just 2,500-3,000 conclusions in the United States every year. There was a spike in reported determinations somewhere around 1970 and 1984, which has been credited to the inertness period in the middle of analysis and the stature of modern exposures, which happened about 40-60 years preceding this time. While presentation was normal over the United States in about all commercial enterprises, it was especially common in the WWII-period military modern cycle, including naval force shipyards.
In spite of the fact that this growth is significantly more regular in men beyond 60 years old, mesothelioma in ladies and kids has been reported too. Mesothelioma foundations for determination in ladies and youngsters are mostly ascribed to optional introduction to asbestos, as it was not unprecedented for men to bring asbestos over into the home on their bodies or dress.